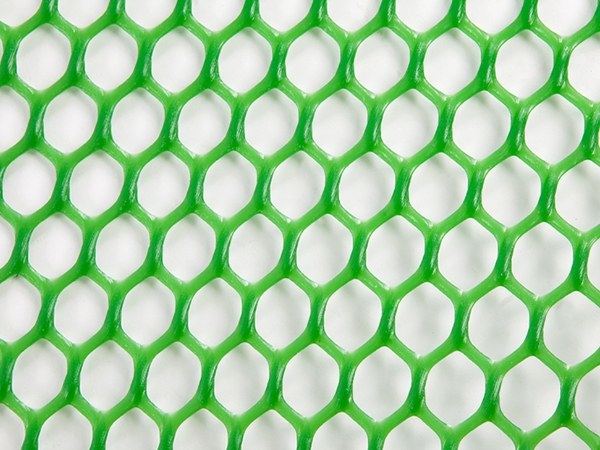
Hexagonal mesh shape
Extruded plastic nets are generally all kinds of plastic nets and net products made of HDPE or PP by extrusion process. During the process, materials melt and form tubular or flat structure with mesh openings.
It has higher tensile strength and tear resistance, and can be cut into any size without damaging its structure.

Extruded plastic net is generally made of PE, PP, PET and other thermoplastic polymers as raw materials added with antioxidants, UV stabilizers, plasticizers, flame retardant, heat stabilizer and other additives, and then is extruded out.
Thermoplastic polymer is a kind of plastic that softens and flows when the temperature rises, and then hardens and maintains its shape at high temperature after cooling. It can be repeatedly processed and molded under certain conditions. Polymer materials are viscoelastic, that is, when the load is unchanged, it will continue to stretch over time and has creep property.
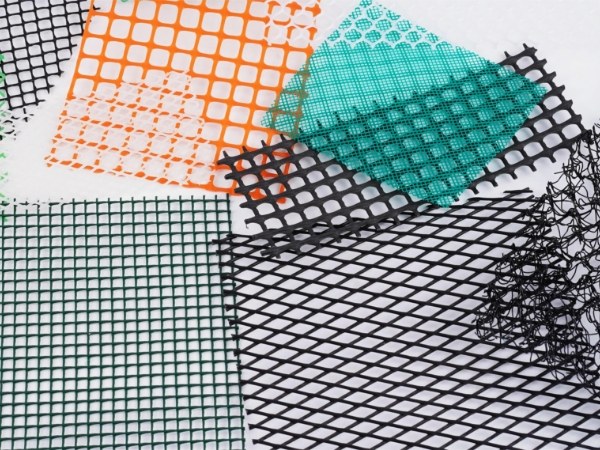

There are some common mesh shapes. Besides, we also provide made-to-order services, for more information, please contact us directly.

Hexagonal mesh shape
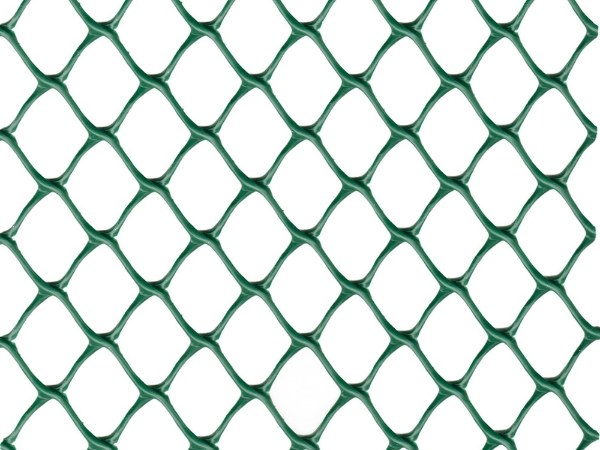
Diamond mesh shape
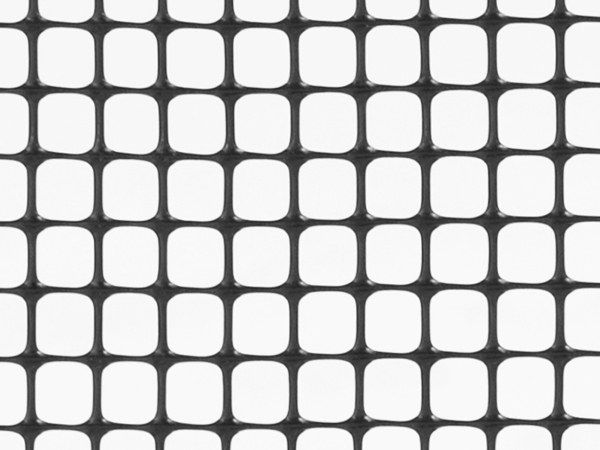
Square mesh shape
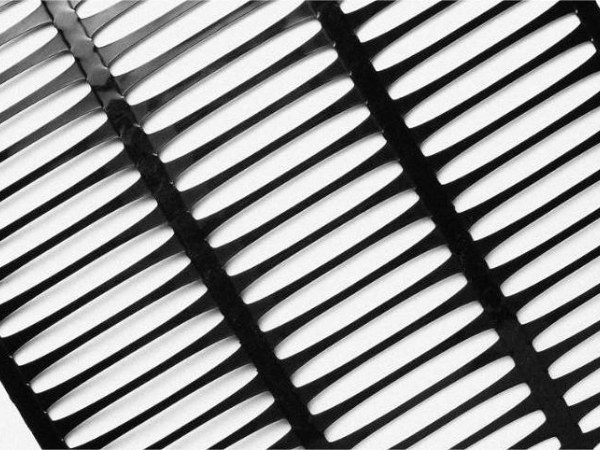

Slotted mesh shape
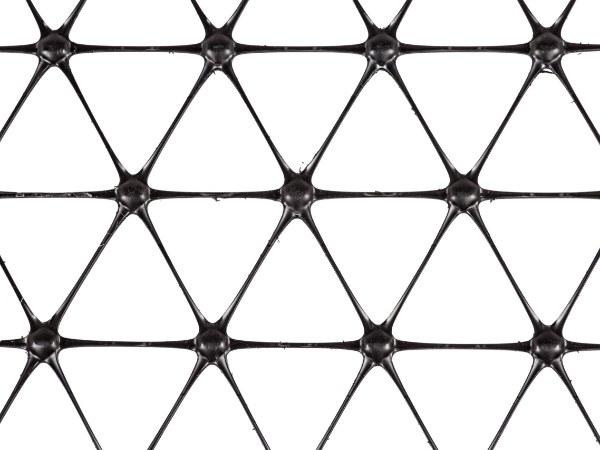
3-way plastic net
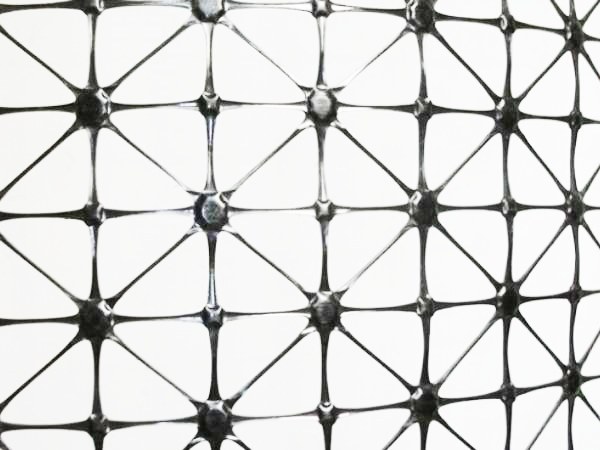
4-way plastic net
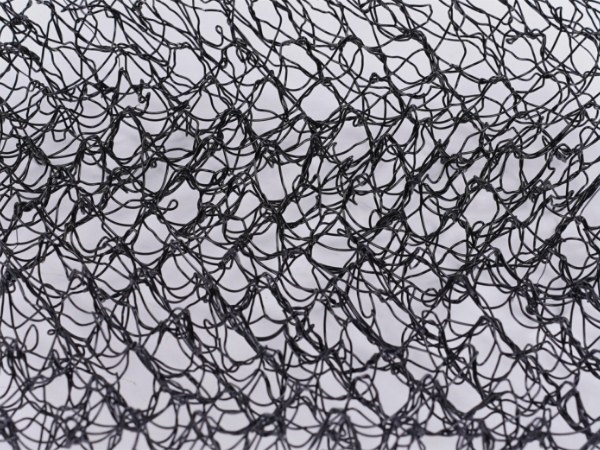

M-shaped 3D plastic mat
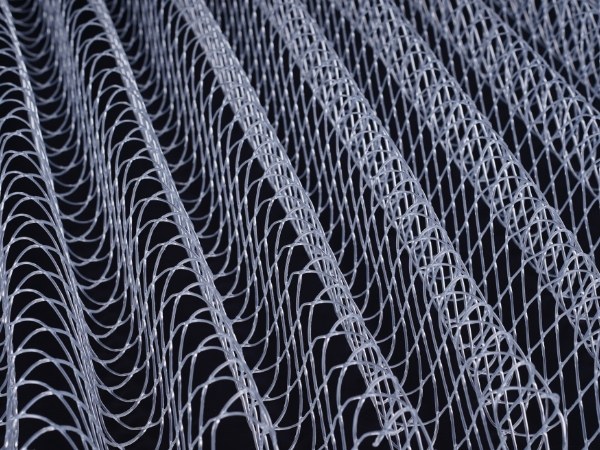
Corrugated plastic net
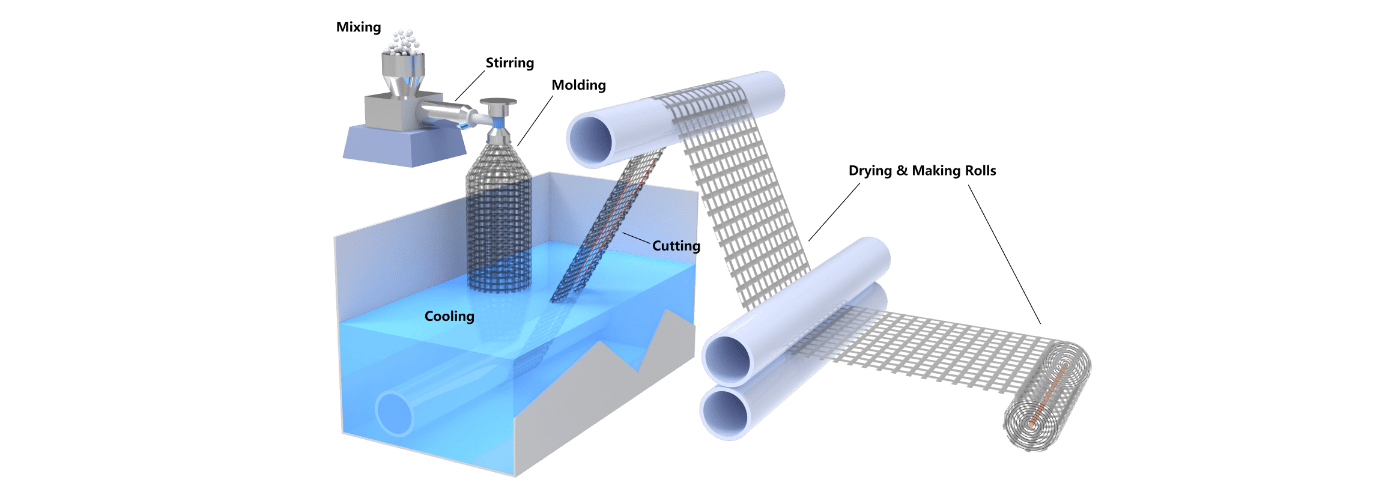
Polymeric molecular chains in a plastic net can be oriented by stretching it under a controlled temperature. This process offers higher tensile strength and weight reduction.
Orientation is the process by which the molecule chains formed by polymers facing the same direction are oriented in a line. To this end, the plastic net must be heated to an optimal temperature to stretch it lengthwise for mono-oriented products and crosswise as well for bi-oriented products. It significantly increases the resistance to traction and reduces the weight of the net by reducing the strand diameter, and is applied to manufacture products intended for specific applications.
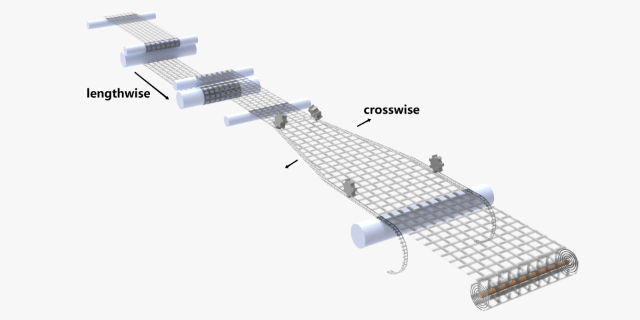
For geotechnical products, extruded plastic net is often used as a support of other material.
The plastic net combines with one or two layers of geosynthetic materials (geotextiles or geomembranes) to form a geocomposite material through heat bonding.
