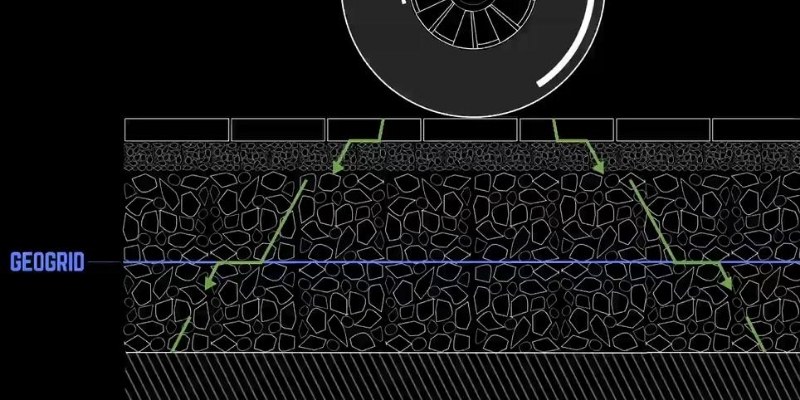
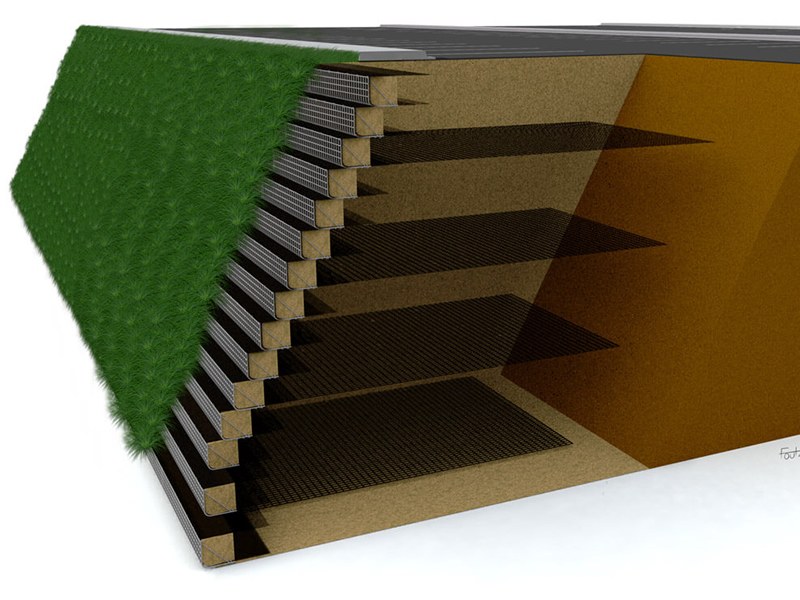
Slope Reinforcement
The required length, vertical distance, number of layers and strength of geogrid vary with every retaining wall project, depending on the specific slope height, load, gradient and water & soil conditions.
For retaining wall taller than 3-feet to 4-feet, it generally requires a licensed professional engineer (P.E., licensed in the state where the project is located at) to do a final wall design and to calculate the desired quantity of geogrid according to the actual field conditions.
Installation steps:
- Excavate the existing soil and then compact and reinforce the excavated area to facilitate the laying of geogrid.
- Cut the geogrid into desired length (embedded depth) and then put it on the compacted soil.
- Drive the pins through the geogrid and the lower-course units for fixing.
- Place and compact the soil backfill above the geogrid, tension the geogrid to avoid wrinkling.
- Place a minimum of 6 inches of soil backfill over the top geogrid layer and then compact it.